Difference between revisions of "Feedback / Microphone"
m ({{Get Plugged In Microphone}}) |
m (new introduction) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr></table> | </tr></table> | ||
| + | |||
Here are some notes about feedback. Rather than sending you following links, I've just put things that seemed relevant below. | Here are some notes about feedback. Rather than sending you following links, I've just put things that seemed relevant below. | ||
| − | == My vocal microphone keeps encountering feedback. Is there anything I can do to stop it? == | + | == Before Anything Else == |
| + | Check your gain setup. Take 2 minutes to watch the video (click Steve's picture above). If you are using an L1™ Classic or L1™ Model I follow the instructions exactly as Steve says. For other gear, the principles are still applicable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes from {{Bose}} == | ||
| + | === My vocal microphone keeps encountering feedback. Is there anything I can do to stop it? === | ||
From the Official Product Troubleshooting Page <ref>[http://www.bose.com/controller?event=VIEW_STATIC_PAGE_EVENT&url=/musicians/support/troubleshooting.jsp&ck=0#feedback Official Product Troubleshooting Pages]</ref>. | From the Official Product Troubleshooting Page <ref>[http://www.bose.com/controller?event=VIEW_STATIC_PAGE_EVENT&url=/musicians/support/troubleshooting.jsp&ck=0#feedback Official Product Troubleshooting Pages]</ref>. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 25: | ||
* Try a different microphone such as a directional mic. Hypercardioid microphones work well with the system. | * Try a different microphone such as a directional mic. Hypercardioid microphones work well with the system. | ||
| − | == How do I control feedback that I may get when using microphones? == | + | === How do I control feedback that I may get when using microphones? === |
From the Official Product FAQs <ref>[http://www.bose.com/controller?event=VIEW_STATIC_PAGE_EVENT&url=/musicians/support/product_faqs.jsp&ck=0#question40 Official Product FAQs]</ref>. | From the Official Product FAQs <ref>[http://www.bose.com/controller?event=VIEW_STATIC_PAGE_EVENT&url=/musicians/support/product_faqs.jsp&ck=0#question40 Official Product FAQs]</ref>. | ||
Techniques that control feedback with a conventional system help with the Personalized Amplification System™ approach also. | Techniques that control feedback with a conventional system help with the Personalized Amplification System™ approach also. | ||
| − | * Get close to the microphone. No other technique has a big an impact on feedback. Each halving of distance is approximately another 6 dB of gain before feedback. This means that the difference between working a | + | * Get close to the microphone. No other technique has a big an impact on feedback. Each halving of distance is approximately another 6 dB of gain before feedback. This means that the difference between working a microphone at 2 inches, and 1/4 inch is 18dB! |
* Use a directional microphone. Hypercardioid is better than cardioid, which is way better than omnidirectional. All sound waves impinging on the microphone from a direction other than the intended signal is "noise" and will lower the threshold of feedback. | * Use a directional microphone. Hypercardioid is better than cardioid, which is way better than omnidirectional. All sound waves impinging on the microphone from a direction other than the intended signal is "noise" and will lower the threshold of feedback. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 47: | ||
| − | + | == Other general notes == | |
| − | * All players should be playing / singing through the | + | * All players should be playing / singing through the L1™ System closest to them |
* Every doubling of distance between the microphone and the singer reduces gain-before-feedback by a factor of 4. The difference between 1/2 inch and an inch can be significant. | * Every doubling of distance between the microphone and the singer reduces gain-before-feedback by a factor of 4. The difference between 1/2 inch and an inch can be significant. | ||
| − | * Wherever possible "acoustic" instruments should use pickups instead of microphones. This is important because many players find it a struggle to keep a | + | * Wherever possible "acoustic" instruments should use pickups instead of microphones. This is important because many players find it a struggle to keep a consistent and close distance between the microphone and their instrument. Also, an instrument can be a source of feedback as it resonates with the amplified sound. |
| − | * Another (low | + | * Another (low priority) design guide-line could be to keep open microphones as far apart as possible. Neighboring systems with open microphones can mutually decrease gain-before-feedback |
| − | |||
| − | + | === Handling the Microphone === | |
shure.com notes <ref>[http://www.shure.com/shurenotes/how_june2004/default.asp Miking Live Vocals - from shure.com]</ref> | shure.com notes <ref>[http://www.shure.com/shurenotes/how_june2004/default.asp Miking Live Vocals - from shure.com]</ref> | ||
| − | Seems like a pretty natural thing, doesn't it? But how your vocalists handle the | + | Seems like a pretty natural thing, doesn't it? But how your vocalists handle the microphone has a major effect on the resulting sound. It may look great, but your tech team won't get the sound they want when your soloist holds a microphone an arm's length from her mouth. |
=== Why? === | === Why? === | ||
| Line 62: | Line 66: | ||
The first reason is the inverse square law. If you hold your mic a half-inch from your lips it receives a given amount of sound energy from your voice. Move it twice as far-one inch-and it receives one-fourth as much energy. That extra half -inch takes away three-quarters of the efficiency of your sound system. While good mic technique involves "working" the microphone, singers that fully extend their arms when reaching for that climax, are usually doing it for dramatic effect. Small changes in distance from the mouth can result in very dramatic changes in sound level. | The first reason is the inverse square law. If you hold your mic a half-inch from your lips it receives a given amount of sound energy from your voice. Move it twice as far-one inch-and it receives one-fourth as much energy. That extra half -inch takes away three-quarters of the efficiency of your sound system. While good mic technique involves "working" the microphone, singers that fully extend their arms when reaching for that climax, are usually doing it for dramatic effect. Small changes in distance from the mouth can result in very dramatic changes in sound level. | ||
| − | Second: When you move the | + | Second: When you move the microphone away from your lips, you must turn up the microphone level at the mixer to be heard, and more unwanted sound enters the mic. When sound from a monitor speaker enters the microphone , it instantly becomes the earsplitting screech we know as feedback. Keeping the microphone close to your mouth minimizes feedback. |
Revision as of 23:40, 3 June 2007
|
Proper Gain Staging is essential to avoiding feedback. Please take 2 minutes to review this short video. Although this is based on the Classic and Model I, the principles are generally applicable. Gain setup for a vocal microphone |
Here are some notes about feedback. Rather than sending you following links, I've just put things that seemed relevant below.
Before Anything Else
Check your gain setup. Take 2 minutes to watch the video (click Steve's picture above). If you are using an L1™ Classic or L1™ Model I follow the instructions exactly as Steve says. For other gear, the principles are still applicable.
Notes from Bose®
My vocal microphone keeps encountering feedback. Is there anything I can do to stop it?
From the Official Product Troubleshooting Page [1].
- Orient the microphone so that it is not pointing directly at your Cylindrical Radiator™ loudspeaker. It’s best when your system is not directly behind you- give greater than 5 feet distance between you and your system.
- Try using a “close-miking” technique to increase the gain at the microphone and to reduce unwanted stage sound.
- Use the HIGH tone control knob for the microphone channel carefully. Feedback could occur when this is set too high.
- Upgrade your power stand to newer software that offer a high gain preset. see: Software Upgrading (This covers firmware update and Version 2.0 Presets)
- If using a vocal effects processor, make sure that it is not contributing to the feedback problem.
- If stand -mounting a directional microphone, tilt the microphone up ten or twenty degrees off the horizon so that it is less sensitive to direct sound from the speakers.
- Try a different microphone such as a directional mic. Hypercardioid microphones work well with the system.
How do I control feedback that I may get when using microphones?
From the Official Product FAQs [2].
Techniques that control feedback with a conventional system help with the Personalized Amplification System™ approach also.
- Get close to the microphone. No other technique has a big an impact on feedback. Each halving of distance is approximately another 6 dB of gain before feedback. This means that the difference between working a microphone at 2 inches, and 1/4 inch is 18dB!
- Use a directional microphone. Hypercardioid is better than cardioid, which is way better than omnidirectional. All sound waves impinging on the microphone from a direction other than the intended signal is "noise" and will lower the threshold of feedback.
- Use as few open microphones as possible. When a microphone is not in use, turn it off.
- When stand mounting a directional microphone, tilt the microphone up ten or twenty degrees off the horizon so that it is less sensitive to direct sound from the speakers.
- Use the HIGH tone control knob for the microphone channel carefully. Feedback could occur when this is set too high.
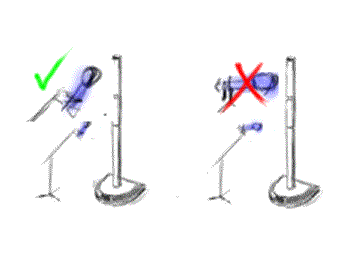
Microphone on a Stand
Here's a sketch of setting up a microphone on stand.
Other general notes
- All players should be playing / singing through the L1™ System closest to them
- Every doubling of distance between the microphone and the singer reduces gain-before-feedback by a factor of 4. The difference between 1/2 inch and an inch can be significant.
- Wherever possible "acoustic" instruments should use pickups instead of microphones. This is important because many players find it a struggle to keep a consistent and close distance between the microphone and their instrument. Also, an instrument can be a source of feedback as it resonates with the amplified sound.
- Another (low priority) design guide-line could be to keep open microphones as far apart as possible. Neighboring systems with open microphones can mutually decrease gain-before-feedback
Handling the Microphone
shure.com notes [3]
Seems like a pretty natural thing, doesn't it? But how your vocalists handle the microphone has a major effect on the resulting sound. It may look great, but your tech team won't get the sound they want when your soloist holds a microphone an arm's length from her mouth.
Why?
The first reason is the inverse square law. If you hold your mic a half-inch from your lips it receives a given amount of sound energy from your voice. Move it twice as far-one inch-and it receives one-fourth as much energy. That extra half -inch takes away three-quarters of the efficiency of your sound system. While good mic technique involves "working" the microphone, singers that fully extend their arms when reaching for that climax, are usually doing it for dramatic effect. Small changes in distance from the mouth can result in very dramatic changes in sound level.
Second: When you move the microphone away from your lips, you must turn up the microphone level at the mixer to be heard, and more unwanted sound enters the mic. When sound from a monitor speaker enters the microphone , it instantly becomes the earsplitting screech we know as feedback. Keeping the microphone close to your mouth minimizes feedback.
See the whole article: Miking Live Vocals
Other References
- Microphone Techniques for Live Sound Reinforcement Shure Educational Publication 2006 39 pages - pdf format
ST 15:46, 22 August 2006 (GMT-7)